Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ito, Fuyumi; Nishimura, Akihiko
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(4), p.667 - 672, 2013/12
We are proposing Magnetic particle Testing (MT) using fabricated micro capsules by the hand-shake method. Here a test piece magnetized beforehand is immersed in liquid dispersed with magnetic particles. Fluorescent pigment adheres to the magnetic particles. So, MT is able to facilitate the crack visually as long as a certain amount of magnetic particles are holding the fluorescent pigment. However, separation between particle and pigment degrades transparency in liquid. Finally the hazy liquid makes difficult to find any crack. To solve this problem, we propose to use the Magnetic Particle Micro Capsule (MPMC). In addition, to applying this MPMC, the surround of the nuclear power plant should be confirmed. To confirm inside wall, the Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) was applied.
Kada, Wataru; Sato, Takahiro; Yokoyama, Akihito; Koka, Masashi; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(3), p.443 - 446, 2013/09
Microscopic imaging and analysis techniques are increasing its importance and being interested from the environmental research fields especially for the target with a complex elemental or chemical structures. Electron or synchrotron-radiation microbeam probes are quite poplar scanning analytical probing techniques for the imaging of such microscopic targets. On the other hand, microbeam techniques using MeV ions have also utilized for such analysis purpose with advantages in the aspect of sensitivity and S/N ratios. However, these Ion Beam Analysis (IBA) techniques like PIXE (Particle Induced X-ray Emission) do not have enough sensitivity in the chemical-state analysis. This limits the application area of IBA techniques compared to the other beam probes. In this study, an new ion microbeam technique with Microscopic by spectroscopic analysis of IL was developed and combined with micro-PIXE system for the simultaneous analysis and imaging of chemical-state distribution in microscopic targets. Spectroscopy of IL from the National Institute of Environmental Science (NIES) aerosol standards was first achieved to visualize chemical state distribution in such microscopic analytical targets with spatial resolution of 1 m.
m.
Kada, Wataru; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Iwamoto, Naoya; Onoda, Shinobu; Grilj, V.*; Skukan, N.*; Makino, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Sato, Takahiro; Jak i
i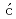 , M.*; et al.
, M.*; et al.
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(2), p.279 - 282, 2013/07
Diamond is interested by many researchers as an excellent candidate material with advantages in the radiation-hardness. For the time-resolved detection of single-ions with several hundred MeV, transmission E detector using thin film CVD diamond is now under investigation for the futuristic utilization in a microbeam line of the AVF cyclotron at JAEA/Takasaki TIARA facility as replacing materials of the beam extraction window. In this research, a Single Crystalline (SC) 50 m thick CVD diamond film ion detector was fabricated for the investigation of the responses and radiation hardness under the focused ion microbeam irradiation. Transient Ion Beam Induced Current (TIBIC) experiment was executed by single hit irradiation of 15 MeV O scanning area of 50
scanning area of 50  m
m and the transient signals with time width of several nano-secounds were consecutively recorded by a high speed (15 GHz) Digital Storage Oscilloscope during the irradiation. The decreases in the individual pulse height was observed by increasing the total amount of the ion dose irradiated in the focused area. These changes were recovered in temporal conversion of applied bias voltages thus trend of decrease were able to be controlled by changing bias settings and irradiation conditions during the experiments.
and the transient signals with time width of several nano-secounds were consecutively recorded by a high speed (15 GHz) Digital Storage Oscilloscope during the irradiation. The decreases in the individual pulse height was observed by increasing the total amount of the ion dose irradiated in the focused area. These changes were recovered in temporal conversion of applied bias voltages thus trend of decrease were able to be controlled by changing bias settings and irradiation conditions during the experiments.
Kitamura, Akane; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.101 - 104, 2013/03
Hamamoto, Satoshi*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Hojo, Kiichi
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.89 - 92, 2013/03
Hamamoto, Satoshi*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Hojo, Kiichi
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.89 - 92, 2013/03
Semiconducting silicides, such as  -FeSi
-FeSi , BaSi
, BaSi and Mg
and Mg Si are quite attractive for their potential as optoelectronic, photovoltaic and thermoelectric materials. Authors have shown that thin, uniform and highly-oriented
Si are quite attractive for their potential as optoelectronic, photovoltaic and thermoelectric materials. Authors have shown that thin, uniform and highly-oriented  -FeSi
-FeSi films can be fabricated on Si (100) substrates with an atomically flat interface, when the substrates are pre-treated with low-energy ions. Since the use of ion beam introduces irradiation defects to the substrate and the film, semiconducting properties may be affected by such defects. Dependence of the crystalline properties of
films can be fabricated on Si (100) substrates with an atomically flat interface, when the substrates are pre-treated with low-energy ions. Since the use of ion beam introduces irradiation defects to the substrate and the film, semiconducting properties may be affected by such defects. Dependence of the crystalline properties of  -FeSi
-FeSi films on the irradiated fluence of sputter etching (SE) of the substrate was investigated to discuss whether it is possible to obtain high crystalline
films on the irradiated fluence of sputter etching (SE) of the substrate was investigated to discuss whether it is possible to obtain high crystalline  -FeSi
-FeSi thin film with very low defect concentration.
thin film with very low defect concentration.
Kato, Sho; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.81 - 84, 2013/03
Nanoparticles were formed by 100 keV tungsten-ion implantation in unpolished glassy carbon substrates at nominal fluences of 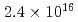 -
- 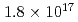 ions/cm
ions/cm . The implanted samples were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, hydrodynamic voltammetry using a rotating disk electrode, and field emission scanning electron microscopy. A significant sputtering effect changed the depth profile during the course of irradiation and limited the amount of tungsten retainable in the substrate in agreement with our calculated distributions. The nanoparticles were composed of tungsten carbide and dispersed uniformly with diameters of around 10 nm.
. The implanted samples were analyzed by Rutherford backscattering spectrometry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, hydrodynamic voltammetry using a rotating disk electrode, and field emission scanning electron microscopy. A significant sputtering effect changed the depth profile during the course of irradiation and limited the amount of tungsten retainable in the substrate in agreement with our calculated distributions. The nanoparticles were composed of tungsten carbide and dispersed uniformly with diameters of around 10 nm.
Nuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu; Sawada, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Shin; Maekawa, Yasunari; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 38(1), p.105 - 108, 2013/03
We report here how conditions of the conductometric analysis affected the etching characteristics of 25  m-thick poly(vinylidene fluoride) film irradiated with 450 MeV
m-thick poly(vinylidene fluoride) film irradiated with 450 MeV  Xe ions. The etching was performed in a 9 mol dm
Xe ions. The etching was performed in a 9 mol dm aqueous potassium hydroxide solution at 80
aqueous potassium hydroxide solution at 80 C in a conductometric cell. According to the scanning electron microscope observations, the ion-track membrane obtained with an applied AC voltage of 1.0 V had the surface pores of 168
C in a conductometric cell. According to the scanning electron microscope observations, the ion-track membrane obtained with an applied AC voltage of 1.0 V had the surface pores of 168 20 nm in diameter. On the other hand, the etching without an applied voltage gave the approximately two-thirds smaller pores. The conductomeric etching would provide a higher degree of freedom for controlling the pore diameter.
20 nm in diameter. On the other hand, the etching without an applied voltage gave the approximately two-thirds smaller pores. The conductomeric etching would provide a higher degree of freedom for controlling the pore diameter.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Yoshii, Kenji; Suzuki, Chikashi
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 37(4), p.579 - 582, 2012/12
We performed X-ray Emission spectroscopy (XES) by using a double crystal spectrometer. Ta-L and L
and L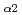 emission lines of Ta-related materials of Ta-metal, Ta
emission lines of Ta-related materials of Ta-metal, Ta O
O , LiTaO
, LiTaO , and KTaO
, and KTaO were measured. XES is one of the most important spectroscopies to make a remarkable progress utilizing third generation synchrotron radiation sources. Here, I discuss some aspects of XES in Ta compounds of recent experimental data. We also discuss an azimuth dependence of resonant X-ray emission spectra (RXES) of a single-crystal KTaO
were measured. XES is one of the most important spectroscopies to make a remarkable progress utilizing third generation synchrotron radiation sources. Here, I discuss some aspects of XES in Ta compounds of recent experimental data. We also discuss an azimuth dependence of resonant X-ray emission spectra (RXES) of a single-crystal KTaO . The precise measurement by the double crystal spectrometer has observed change of the electronic structure by crystal orientation. Since electronic structure observation is a local probe, it can detect minute lattice deformation.
. The precise measurement by the double crystal spectrometer has observed change of the electronic structure by crystal orientation. Since electronic structure observation is a local probe, it can detect minute lattice deformation.
Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Asano, Atsushi*; Maeyoshi, Yuta*; Marui, Hiromi*; Omichi, Masaaki*; Saeki, Akinori*; Seki, Shuhei*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; et al.
no journal, ,
 m band using proton beam writing
m band using proton beam writingMiura, Kenta*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Koka, Masashi; Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Okubo, Takeru; Yamazaki, Akiyoshi; Kada, Wataru; Yokoyama, Akihito; Kamiya, Tomihiro; et al.
no journal, ,
Yokoyama, Akihito; Kada, Wataru; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Yokota, Wataru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsuru, Tomohito; Aoyagi, Yoshiteru*; Shimokawa, Tomotsugu*; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
Recent progress in grain boundary engineering allows the effective control of grain scale and microstructure in metallic systems, improving bulk material properties. It has been possible to produce nano-crystalline and ultrafine-grained metals with submicron grain size. Mechanical properties of the nano structured metals cannot be predicted based on assumptions of the average quantity of collective motion of dislocations, and therefore it is increasingly necessary to understand the role of each grain and its effect on the plastic deformation. In the present study, a multiscale computational modelling based on atomistic and crystal plasticity (CP) analysis is developed to capture the effect of grain size and macroscopic mechanical properties.
Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Mamiya, Hiroaki*; Terada, Noriki*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Tsujii, Naohito*; Doenni, A.*; Kaneko, Koji; Metoki, Naoto; Igawa, Naoki; et al.
no journal, ,
In this paper, we will demonstrate some application of neutron scattering for magnetic refrigerant materials Ho Pd
Pd and dilute spinel ferrites. In order to determine the magnetic structure, we have performed neutron powder diffraction experiments at JRR-3. The magnetic peaks with a propagation vector k = (0.18, 0.18, 0.18) are gradually developing. The peak width is significantly broader even 5 K, indicating a short-range order with a long wave length.
and dilute spinel ferrites. In order to determine the magnetic structure, we have performed neutron powder diffraction experiments at JRR-3. The magnetic peaks with a propagation vector k = (0.18, 0.18, 0.18) are gradually developing. The peak width is significantly broader even 5 K, indicating a short-range order with a long wave length.
Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Tsukuda, Satoshi*; Seki, Shuhei*
no journal, ,
A ceramic nano fiber was synthesized from a thin film of precursor polymer using ion-beam irradiation techniques. We fabricate the new control method of the nanofiber radius using ion and electron beams irradiation. Polycarbosilane (PCS) film was irradiated by 490 MeV 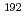 Os
Os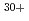 ion beams, subsequently, irradiated by 2 MeV EB. After irradiation, the thin film was developed by solvent, subsequent pyrolysis converted polymeric into inorganic SiC nano fibers. The radius of PCS nano fiber increased with the dose of EB irradiation. The two step irradiation method using ion and electron beams enables to increase the radius of the nano fiber; therefore it has been expected to be a standing nano fiber as high efficiency catalyst materials.
ion beams, subsequently, irradiated by 2 MeV EB. After irradiation, the thin film was developed by solvent, subsequent pyrolysis converted polymeric into inorganic SiC nano fibers. The radius of PCS nano fiber increased with the dose of EB irradiation. The two step irradiation method using ion and electron beams enables to increase the radius of the nano fiber; therefore it has been expected to be a standing nano fiber as high efficiency catalyst materials.
Oshima, Takeshi; Yamamoto, Takashi; Onoda, Shinobu; Abe, Hiroshi; Sato, Shinichiro; Jahnke, K.*; Heller, P.*; Gerstmayr, A.*; H ussler, A.*; Naydenov, B.*; et al.
ussler, A.*; Naydenov, B.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Negatively charged nitrogen-vacancy (NV ) centers were created in high quality IIa diamonds by nitrogen (N) implantation. To identify implanted N atoms and their incident position, micro ion beams of
) centers were created in high quality IIa diamonds by nitrogen (N) implantation. To identify implanted N atoms and their incident position, micro ion beams of  N (natural abundance 0.37%) were applied. Since the reduction of
N (natural abundance 0.37%) were applied. Since the reduction of  C affects an increase in T
C affects an increase in T , N implantation into a CVD diamond with high purity of
, N implantation into a CVD diamond with high purity of  C (99.99%) was carried out. As a result, the value of T
C (99.99%) was carried out. As a result, the value of T for both
for both  NV
NV and
and  NV
NV centers (
centers ( NV
NV centers are created from
centers are created from  N atoms originally existing in the diamond and vacancy introduced by implantation after annealing) was obtained to be about 2 ms. By optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) measurements, the creation yield of both
N atoms originally existing in the diamond and vacancy introduced by implantation after annealing) was obtained to be about 2 ms. By optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) measurements, the creation yield of both  NV
NV and
and  NV
NV was estimated.
was estimated.
Johnson, B. C.; Oshima, Takeshi; McCallum, J. C.*
no journal, ,
Solid phase epitaxy (SPE) is an important process used for the formation of shallow junctions on a low thermal budget. On annealing, atoms reorder at the crystal-amorphous (c-a) interface via a bond breaking mechanism, possibly mediated by dangling bonds. When the c-a interface passes a dopant, it is incorporated onto an electrically active lattice site, shifts the Fermi level and enhances the SPE velocity. The generalized Fermi level shifting (GFLS) model describes this process with two fitting parameters: the energy level, E, and degeneracy, g, of the SPE defect. High dopant concentrations induce a uniaxial strain in the plane of the c-a interface and is also expected to effect the SPE rate. In this study, we successfully incorporate this into the GFLS model. SPE data for a broad range of dopant concentrations and species in both silicon and germanium are investigated. Although the dopant concentrations are similar, the SPE of Ge in Sb rates are noticeably lower. Uniaxial compressive stress arising from the large Sb atoms causes this discrepancy.
Yamamoto, Shunya; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kawaguchi, Kazuhiro; Yoshikawa, Masahito
no journal, ,
For practical use of polymer electrode membrane fuel cells, development of low Pt loading catalysts and non-Pt catalysts for an oxygen reduction reaction have been required. One promising non-Pt catalyst is based on the transition metal(TM)-nitrogen (N)-carbon(C) systems (TM: Fe, Co, Ni, etc.). In the present study, we prepared Fe and N doped carbon film on a glassy carbon (GC) substrate heated at different temperatures in the presence of N gas using a pulsed laser deposition (PLD). The ORR activity of the films was electrochemically determined using a rotating disk electrode system. The ORR activity of Fe-N-C films increased with elevating temperature (700-900
gas using a pulsed laser deposition (PLD). The ORR activity of the films was electrochemically determined using a rotating disk electrode system. The ORR activity of Fe-N-C films increased with elevating temperature (700-900 C) of the GC substrate during the deposition. The Fe-N-C film prepared at 800
C) of the GC substrate during the deposition. The Fe-N-C film prepared at 800 C showed high ORR activity; its ORR potential was 0.76V (vs. NHE). Our preliminary results suggest that suitable concentration of doped Fe and deposition temperature make it possible to improve ORR activity of Fe-N-C films.
C showed high ORR activity; its ORR potential was 0.76V (vs. NHE). Our preliminary results suggest that suitable concentration of doped Fe and deposition temperature make it possible to improve ORR activity of Fe-N-C films.
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Akaoka, Masato*; Tamada, Masao; Mitomo, Hiroshi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) synthesized by polycondensation is a completely biodegradable aliphatic and aromatic polyester. PBAT is decomposed into harmless water and carbon dioxide by microorganisms in the soil. Therefore, PBAT is expected to be utilized for applications in trash bags and disposable packages. The high thermal stability is, however, necessary for expanding their applications. To improve the thermal stability, radiation effect on crosslinking of PBAT was investigated. The PBAT films with and without triallyl isocyanulate (TAIC) as a crosslinker were prepared and then irradiated with electron beam. The gel content was estimated by weighing insoluble part of the crosslinked PBAT film after immersion in chloroform. Gelation of the irradiated PBAT with 3% TAIC is higher than that of PBAT without TAIC at the dose range from 10 to 200 kGy. This result indicates that the crosslinking structures are effectively formed when PBAT films were irradiated with TAIC. The thermal stability of the crosslinked PBAT films was estimated by thermomechanical analyzer. The modified films have excellent properties as demonstrated by retention of original shape even at temperatures higher than melting point (115  C). The biodegradability, which was estimated by enzyme test using Lipase AK, of the crosslinked PBAT film was similar to that of non-irradiated one. As a result, the crosslinked PBAT after usage would undergo biodegradation by naturally existing microorganisms. Therefore, the crosslinked PBAT was found to be thermal stable and biodegradation enough for expanding applications.
C). The biodegradability, which was estimated by enzyme test using Lipase AK, of the crosslinked PBAT film was similar to that of non-irradiated one. As a result, the crosslinked PBAT after usage would undergo biodegradation by naturally existing microorganisms. Therefore, the crosslinked PBAT was found to be thermal stable and biodegradation enough for expanding applications.
Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Sugo, Yumi; Kurashima, Satoshi; Yamashita, Shinichi; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English